Release Date : 2024/04/01
Abdominal pain can be a cause for concern, as it could indicate a variety of underlying conditions, some of which may require prompt medical attention. One such condition is appendicitis, an inflammation of the appendix that can potentially lead to serious complications if left untreated. In the quest to accurately diagnose and treat appendicitis, CT scans have emerged as a powerful diagnostic tool. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the role of CT scans in detecting appendicitis, their benefits, and the importance of timely intervention.
Understanding Appendicitis
Before delving into the role of CT scans, let’s first understand what appendicitis is:
- The appendix is a small, pouch-like structure located at the junction of the small and large intestines.
- Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed, often due to an obstruction or infection.
- If left untreated, the inflamed appendix can rupture, leading to a severe and potentially life-threatening condition called peritonitis.
Common Symptoms of Appendicitis
While CT scans play a crucial role in diagnosis, it’s important to be aware of the common symptoms of appendicitis:
- Abdominal Pain: The most prominent symptom of appendicitis is pain that typically starts around the navel and gradually shifts to the lower right abdomen.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many individuals with appendicitis experience nausea and vomiting, particularly as the condition progresses.
- Loss of Appetite: A loss of appetite is common among those with appendicitis, especially as the pain intensifies.
- Fever: A low-grade fever is often present in cases of appendicitis, indicating an underlying infection.
- Abdominal Swelling or Bloating: As the appendix becomes increasingly inflamed, it can cause swelling or bloating in the abdomen.
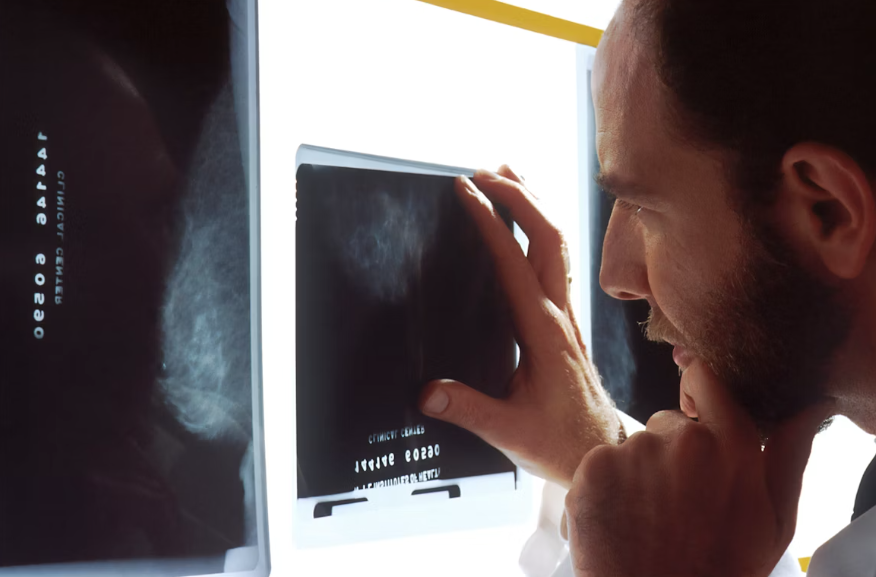
The Role of CT Scans in Diagnosing Appendicitis
CT scans, also known as computed tomography scans, have become an invaluable tool in the diagnosis of appendicitis. Here’s how they work:
- Detailed Imaging: CT scans use X-rays and advanced computer technology to create detailed, cross-sectional images of the body, providing a clear view of the appendix and surrounding structures.
- Identifying Inflammation: The high-resolution images from a CT scan can reveal signs of inflammation, such as swelling or the presence of fluid around the appendix.
- Detecting Complications: CT scans can also detect potential complications of appendicitis, such as an abscess or a perforated (ruptured) appendix.
- Ruling Out Other Conditions: In some cases, CT scans can help rule out other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as ovarian cysts or diverticulitis.
Benefits of CT Scans in Appendicitis Diagnosis
The use of CT scans in diagnosing appendicitis offers several advantages:
- Accuracy: CT scans have a high accuracy rate in detecting appendicitis, reducing the risk of misdiagnosis and unnecessary surgeries.
- Rapid Results: CT scans provide quick results, allowing for timely diagnosis and treatment, which is crucial in preventing potential complications.
- Visualization of Complications: The detailed imaging provided by CT scans can help identify complications associated with appendicitis, such as abscesses or perforations, guiding appropriate treatment decisions.
- Versatility: CT scans can be used to diagnose appendicitis in individuals of all ages, including children and pregnant women (with appropriate precautions).
Preparing for a CT Scan
If your healthcare provider suspects appendicitis and orders a CT scan, there are a few steps you may need to take to prepare:
- Fasting: In some cases, you may be instructed to fast for a certain period before the scan to ensure clear images of the abdominal area.
- IV Contrast: You may receive an intravenous (IV) contrast dye during the CT scan, which helps highlight certain structures and provides better visualization.
- Pregnancy Precautions: If you are pregnant, be sure to inform your healthcare provider, as special precautions may be taken to minimize radiation exposure to the developing fetus.
Interpreting CT Scan Results
The interpretation of CT scan results for appendicitis is typically performed by a radiologist, a medical professional specialized in interpreting medical images:
- Positive Findings: Signs of appendicitis on a CT scan may include an enlarged, thickened, or inflamed appendix, as well as the presence of fluid or abscesses around the appendix.
- Negative Findings: If the CT scan does not show any signs of appendicitis, alternative diagnoses may be considered, or additional testing may be recommended.
- Grading Severity: CT scans can also help determine the severity of appendicitis, which can guide treatment decisions, such as whether surgery is necessary or if antibiotics may be an appropriate option.
Treatment Options Based on CT Scan Findings
The treatment approach for appendicitis may vary depending on the CT scan findings:
- Appendectomy: If the CT scan confirms appendicitis, the standard treatment is an appendectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the inflamed appendix. This can be done through open surgery or laparoscopic (minimally invasive) techniques.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, especially if the appendicitis is caught early or the patient has a high risk for surgery, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the inflammation.
- Monitoring: For mild cases or in certain high-risk individuals, your healthcare provider may opt for close monitoring and observation, especially if the CT scan does not indicate a high risk of rupture.
Potential Complications and Risks
While CT scans are generally safe, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of:
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve the use of ionizing radiation, which can increase the risk of cancer over time, especially with repeated exposure.
- Contrast Dye Reactions: Some individuals may experience an allergic reaction or adverse effects from the contrast dye used during the CT scan.
- False Positives or Negatives: While CT scans are highly accurate, there is a small risk of false positive or false negative results, which can lead to misdiagnosis or unnecessary treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or fever, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. While these symptoms can be attributed to various conditions, they could also be signs of appendicitis or other serious medical issues that require prompt evaluation and treatment.
Other Diagnostic Tools for Appendicitis
While CT scans are widely used in diagnosing appendicitis, there are other diagnostic tools that may be employed, depending on the individual case and available resources:
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal structures and can be useful in detecting appendicitis, particularly in children and pregnant women.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide detailed images of the abdomen and appendix without the use of ionizing radiation, but it is generally more expensive and less widely available than CT scans.
- Blood Tests: Certain blood tests, such as measuring white blood cell count or inflammatory markers, can support the diagnosis of appendicitis but are not definitive on their own.
Seeking Support and Additional Resources
Dealing with appendicitis and undergoing medical procedures can be a stressful and overwhelming experience. It’s important to seek support from friends, family, or support groups to help you navigate the emotional and practical challenges associated with this condition.
Additionally, there are various resources available to help you learn more about appendicitis, CT scans, and digestive health, such as reputable medical websites, patient advocacy organizations, and educational materials provided by healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
CT scans have revolutionized the diagnosis of appendicitis, providing healthcare professionals with a powerful tool to accurately identify inflammation and potential complications. By offering detailed imaging and rapid results, CT scans play a crucial role in guiding appropriate treatment decisions and preventing potentially life-threatening complications associated with appendicitis.
If you experience symptoms that may indicate appendicitis, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Remember, being proactive about your health and seeking professional medical advice is the key to ensuring a successful recovery and maintaining overall well-being.